Market Data

July 6, 2021
Employment by Industry: 850,000 Workers Added to Payrolls in June
Written by David Schollaert
The U.S. labor market accelerated in June, seeing the largest gain in 10 months, reported the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). The latest data shows a surge of 850,000 new workers added to payrolls in June after a spring lull. Wages also saw noticeable improvements, both positive signs of growing demand for workers.
Following a disappointing jobs reports in April, the U.S. labor market has seen more than 1.6 million new jobs added between May and June. Despite the additions in June, labor shortages and enhanced unemployment benefits continued to temper hiring. Once again, leisure and hospitality—the sector hit hardest by the pandemic—led the payroll recovery in June, adding 343,000 jobs as pandemic-related restrictions continued to ease in some parts of the country. Also seeing job growth were public and private education, professional and business services, retail trade and other services.
The unemployment rate edged up to 5.9% in June from 5.8% the month prior. That was in part because of a positive development: A modest number of Americans came off the sidelines and entered the job search, expanding the labor pool. A broader measure of unemployment that considers workers stuck in part-time jobs and those too discouraged to look for work fell sharply last month.
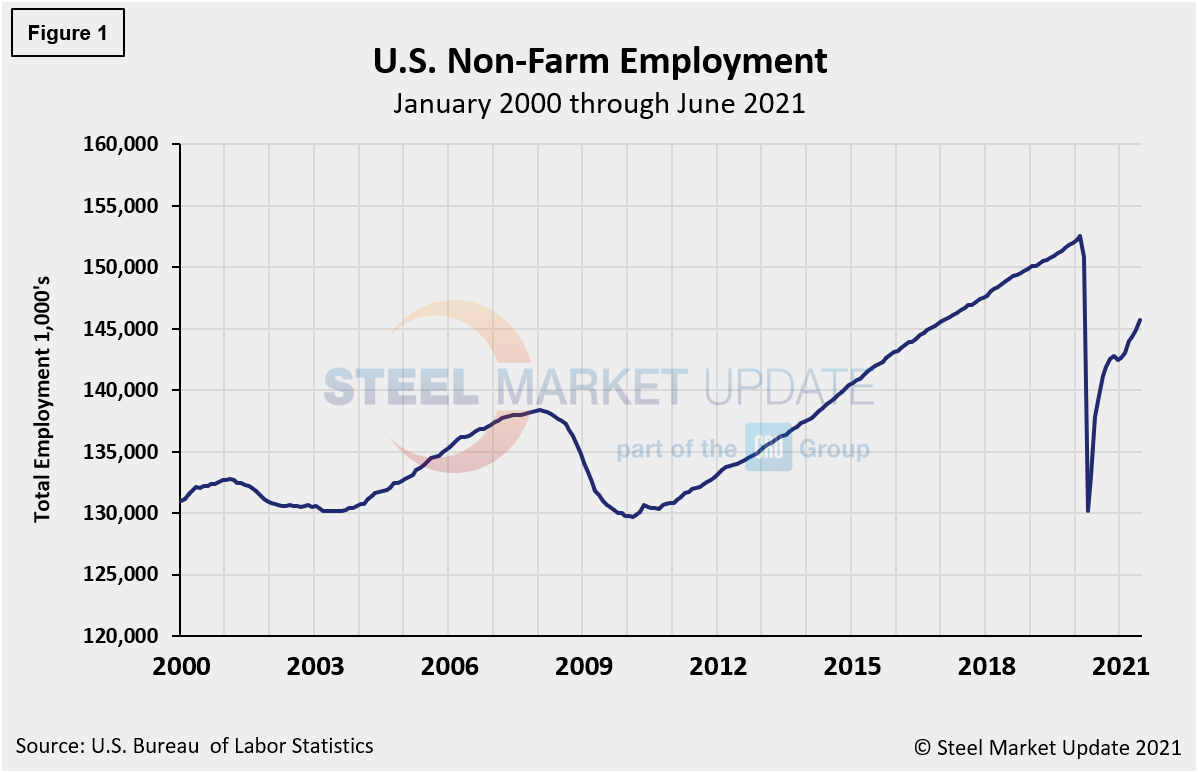
The number of unemployed persons rose by 233,000 to 9.5 million last month. To date, the U.S. has recovered 13.0 million, or 58%, of the 22.5 million jobs lost last spring, leaving the nation approximately 6.7 million jobs below its pre-pandemic level, when the unemployment rate was just 3.5%. Figure 1 shows the total number of people employed in the nonfarm economy.
Designed on rolling time periods of 1 month, 3 months, 1 year and 2 years, the table below breaks total employment into service industries and goods-producing industries, and then into private and government employees. Most of the goods-producing employees work in manufacturing and construction. Comparing service and goods-producing industries in June shows service jobs to have increased by 0.7%, while goods-producing jobs rose by 0.1% from May’s result. Note, the subcomponents of both manufacturing and construction shown in this table don’t add up to the total because we have only included those with the most relevance to the steel industry.
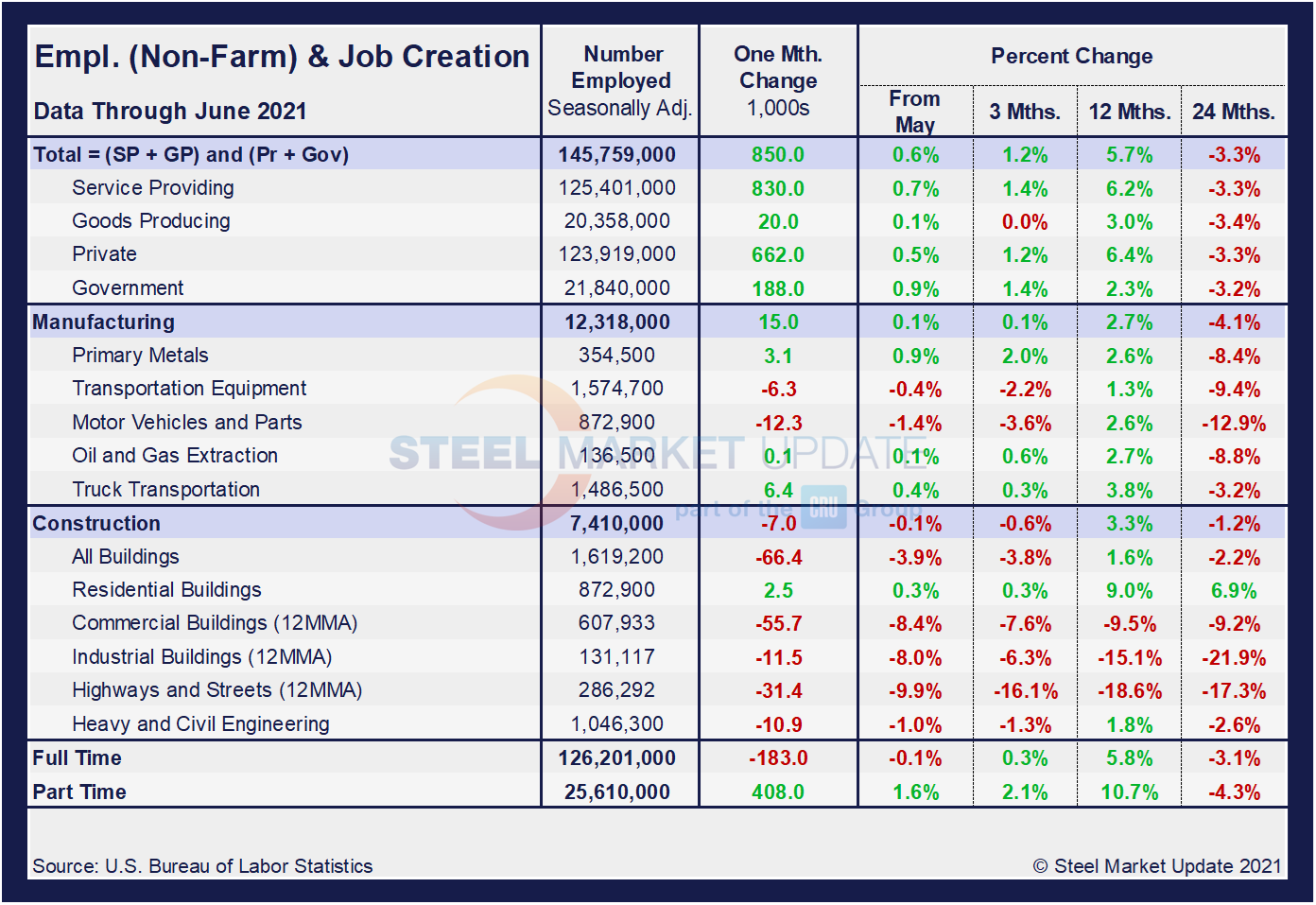
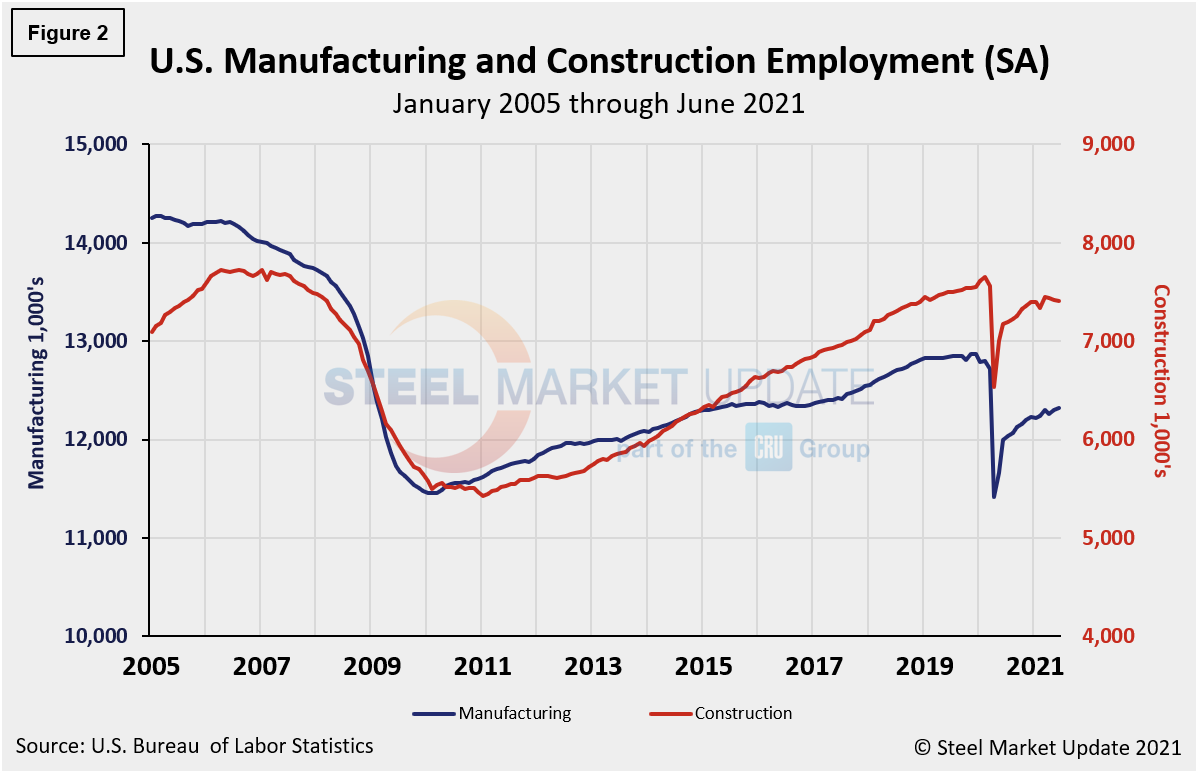
Comparing June to May, manufacturing employment was up 0.1% versus unchanged the month prior. Construction was down 0.1% month on month after dipping 0.4% in May. Despite the repeated gains in May and June, the inconsistencies and struggles across many subcomponents since the beginning of the year point to the significant obstacles facing the U.S. economy and domestic job creation. And three-month, 12-month and 24-month comparisons remain problematic due to the extensive losses resulting from pandemic. In the year-over-year contrast, manufacturing is up just 2.7% and construction is up 3.3%. Further growth is still expected as the marketplace advances from the freefall seen during the second quarter of 2020.
Manufacturing employment increased by 15,000 in June compared to an increase of 6,000 the month prior, led by an increase of 9,000 in furniture and related products, 6,000 in fabricated metal products, and 3,000 in primary metals, which were partially offset by a loss of 12,000 in motor vehicles and parts. Employment in manufacturing is down by 481,000 from its level in February 2020. Construction employment was down by 7,000 month on month following a decrease of 29,000 in May, led by nonresidential specialty trade contractors and heavy and civil engineering construction jobs. Employment in the construction industry overall is still 238,000 below its February 2020 level, according to the BLS data. Figure 2 shows the history of employment in manufacturing and construction since January 2005.
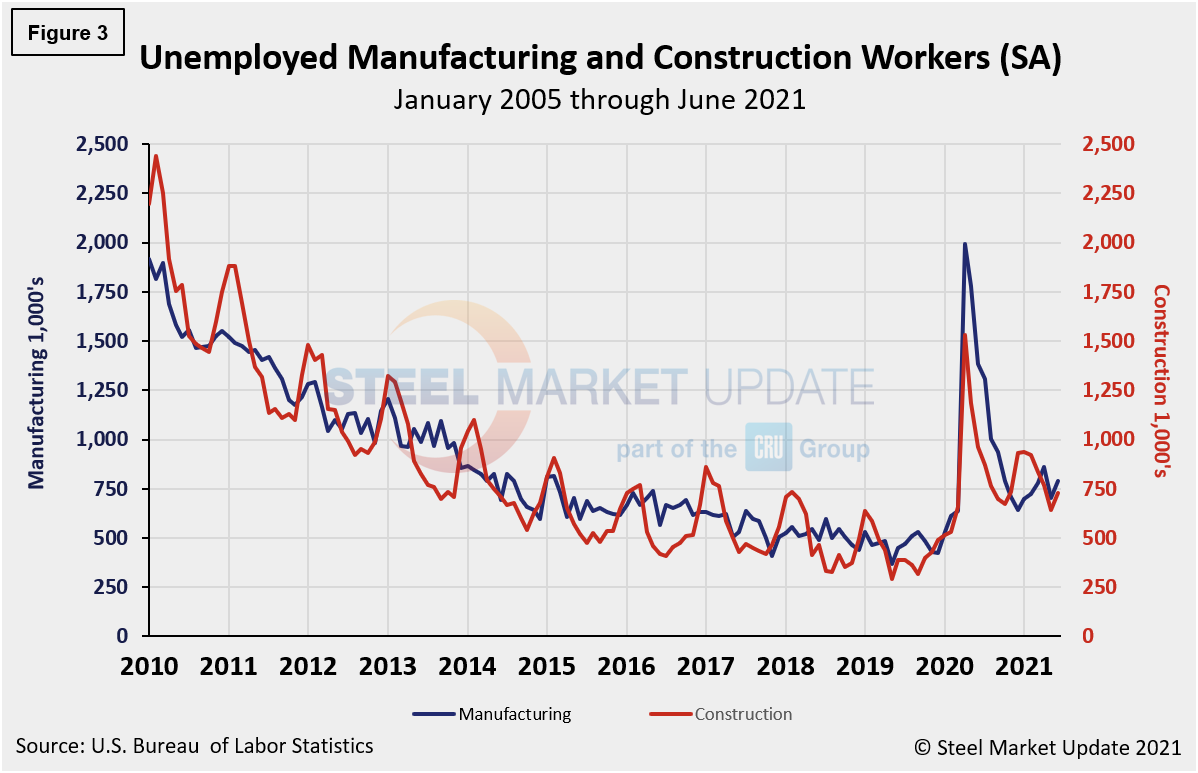
The reported number of unemployed manufacturing and construction workers is shown in Figure 3. Both manufacturing and construction unemployment increased in June. Manufacturing’s unemployed persons increased from 705,000 in May to 792,000, a 12.3% increase month on month. Construction unemployment rose 13.7% month on month, from 642,000 in May to 730,000 in June.
Explanation: On the first or second Friday of each month, the Bureau of Labor Statistics releases the employment data for the previous month. Data is available at www.bls.gov. The BLS employment database is a reality check for other economic data streams such as manufacturing and construction. It is easy to drill down into the BLS database to obtain employment data for many subsectors of the economy. The important point about all these data streams is not necessarily the nominal numbers, but the direction in which they are headed.
By David Schollaert, David@SteelMarketUpdate.com







