Market Data

June 28, 2022
May Durable Goods Surprise, Beat Forecast
Written by David Schollaert
New orders for US manufactured durable goods rose more than expected in May, suggesting business investment remains resilient even in the face of deteriorating business and consumer sentiment as well as heightened fears of a recession.
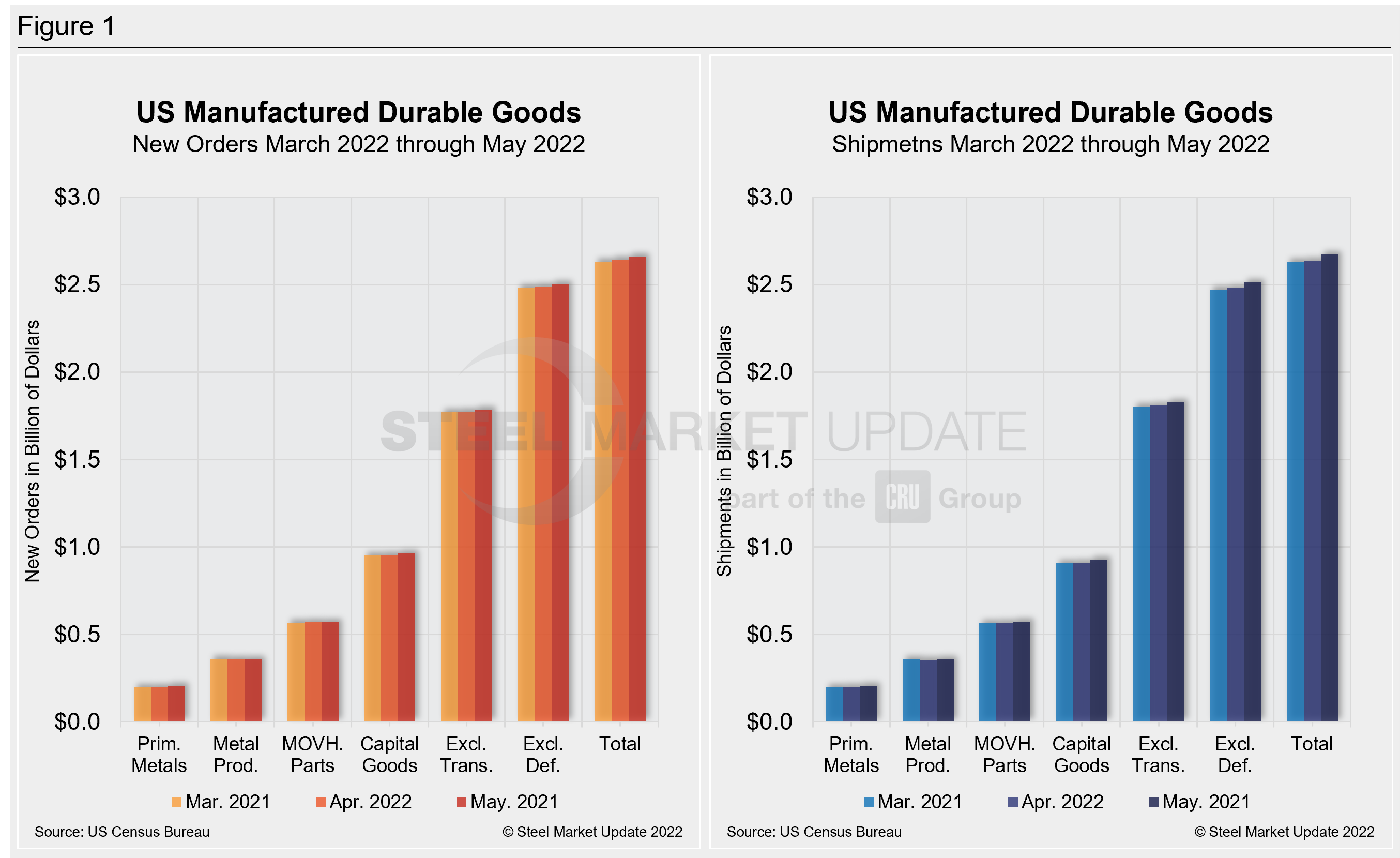
![]() Last month’s bookings for durable goods rose 0.7% following a revised 0.4% decline a month earlier, according to the Commerce Department. Figures are not adjusted for inflation
Last month’s bookings for durable goods rose 0.7% following a revised 0.4% decline a month earlier, according to the Commerce Department. Figures are not adjusted for inflation
The value of core capital goods orders – a proxy for investment in equipment that excludes aircraft and non-defense capital goods – expanded by 0.5% in May, accelerating from a 0.3% gain in April. Those orders were up 10.2% year-on-year (YoY) last month.
Core capital goods shipments, a figure that is used to help calculate equipment investment in the government’s gross domestic product report, rose 0.8% in May. Despite some boost from higher prices, shipments still showed strength after adjusting for inflation.
The broad-based gain in durable goods included strong bookings for primary metals as well as computers and electronic products. But orders for electrical equipment, appliances, and components fell 0.9%, while demand for fabricated metal products was unchanged.
The better-than-expected increase in core capital goods orders underscored underlying strength in manufacturing, which accounts for 12% of the economy, despite weak factory surveys.
Below is the May advance report from the US Census Bureau on durable goods manufacturers’ shipments, inventories, and orders:
New Orders
New orders for manufactured durable goods in May increased $1.9 billion or 0.7% to $267.2 billion, the US Census Bureau announced today. This increase, up seven of the last eight months, followed a 0.4% April increase. Excluding transportation, new orders increased 0.7%. Excluding defense, new orders increased 0.6%. Transportation equipment, up two consecutive months, led the increase, $0.7 billion or 0.8% to $87.6 billion.
Shipments
Shipments of manufactured durable goods in May, up twelve of the last thirteen months, increased $3.6 billion or 1.3% to $268.4 billion. This followed a 0.3% April increase. Transportation equipment, up seven of the last eight months, led the increase, $1.7 billion or 2.1% to $84.7 billion.
Unfilled Orders
Unfilled orders for manufactured durable goods in May, up twenty-one consecutive months, increased $3.7 billion or 0.3% to $1,109.8 billion. This followed a 0.5% April increase. Transportation equipment, up fifteen of the last sixteen months, led the increase, $2.9 billion or 0.5% to $639.8 billion.
Inventories
Inventories of manufactured durable goods in May, up sixteen consecutive months, increased $2.7 billion or 0.6% to $482.7 billion. This followed a 0.9% April increase. Machinery, up nineteen consecutive months, led the increase, $1.0 billion or 1.2% to $82.3 billion.
Capital Goods
Nondefense new orders for capital goods in May increased $0.4 billion or 0.5% to $83.7 billion. Shipments increased $1.3 billion or 1.6% to $79.8 billion. Unfilled orders increased $3.9 billion or 0.6% to $623.8 billion. Inventories increased $0.6 billion or 0.3% to $210.7 billion.
Defense new orders for capital goods in May increased $0.3 billion or 2.6% to $13.7 billion. Shipments increased $0.3 billion or 2.5% to $14.0 billion. Unfilled orders decreased $0.2 billion or 0.1% to $185.6 billion. Inventories increased $0.1 billion or 0.3% to $22.3 billion.
Revised and Recently Benchmarked April Data
Revised seasonally adjusted April figures for all manufacturing industries were: new orders, $534.8 billion (revised from $533.2 billion); shipments, $534.3 billion (revised from $532.1 billion); unfilled orders, $1,106.1 billion (revised from $1,106.8 billion) and total inventories, $787.9 billion (revised from $786.1 billion).
By David Schollaert, David@SteelMarketUpdate.com







