Market Data

October 10, 2019
Net Job Creation Through September 2019
Written by Peter Wright
The rate of job creation in September slowed to 136,000, but the details of job cuts and job openings continue to be historically very positive, according to Steel Market Update’s analysis of the latest Bureau of Labor Statistics data.
Net job creation in September declined to 136,000 from an upwardly revised 168,000 in August. July was revised up by 7,000 and August up by 38,000. Rising employment and wages are the main contributors to GDP growth because personal consumption accounts for almost 70 percent of GDP. Steel consumption is related to GDP; therefore, this is one of the indicators that help us understand the reality of the steel market.
Figure 1 shows the three-month moving average (3MMA) of the number of jobs created monthly since 2000 as the brown bars and the total number employed as the black line. Economy.com reported as follows: “Payrolls increased by 136,000 in September, in line with the modest expectations of the slowing labor market, but one that is growing more than adequately enough to keep pace with labor force trends. As such, the unemployment rate fell to a new cyclical low of 3.5%. The private sector added only 114,000 jobs. Average hourly earnings slipped slightly, yielding a year-over-year gain of 2.9 percent. Thus, wage pressures are not intensifying.”
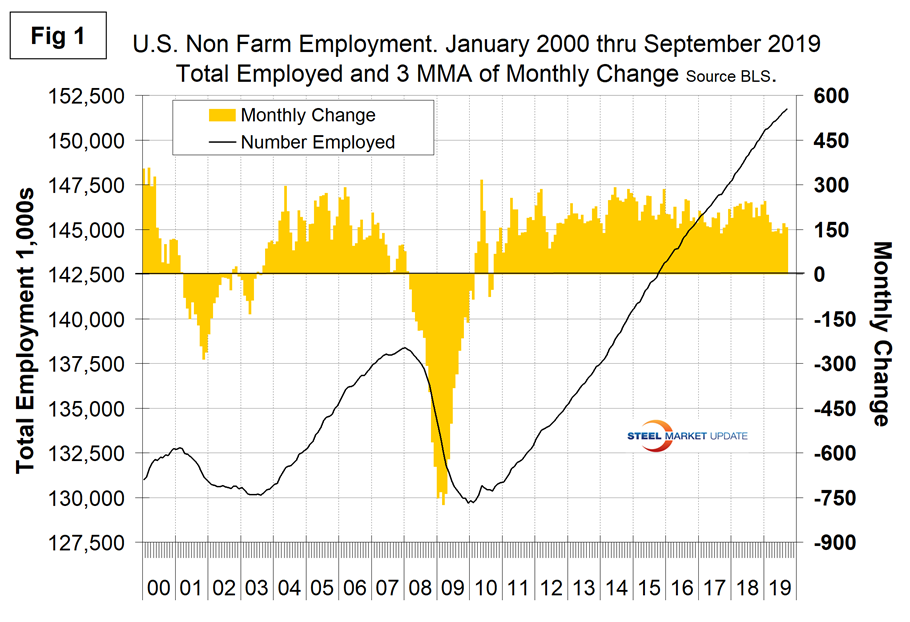
We prefer to use three-month moving averages in our analyses to reduce short-term variability. In averaging employment statistics in this way, we even out what is notoriously volatile data.
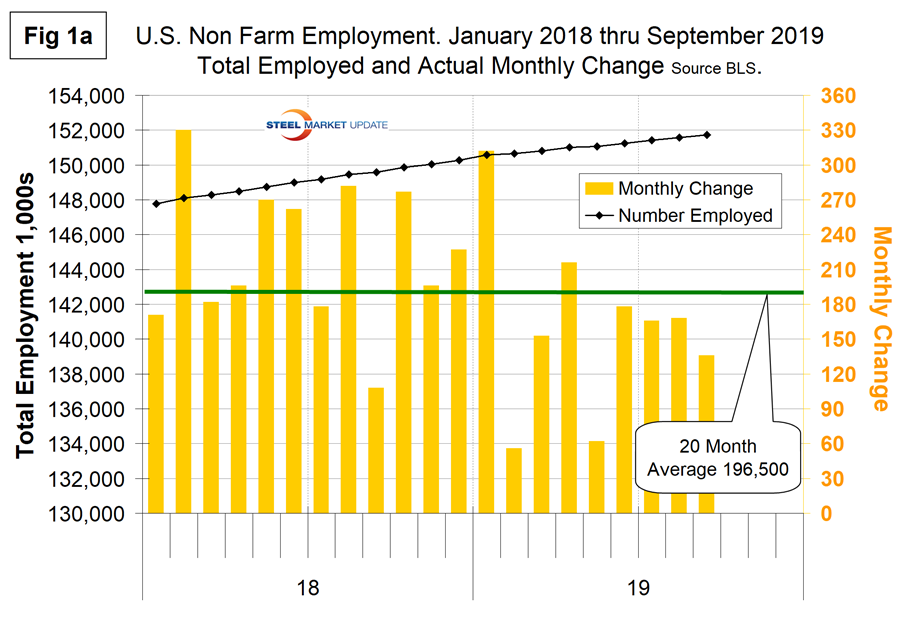
Figure 1a shows the raw monthly data since January last year and that the variability in the data has been worse in 2019 than it was in 2018. The average monthly job creation in the last 21 months has been 196,500. In 2018, the average rate of job creation was 223,300 per month. In the first nine months of 2019, the average monthly rate was 160,800 jobs.
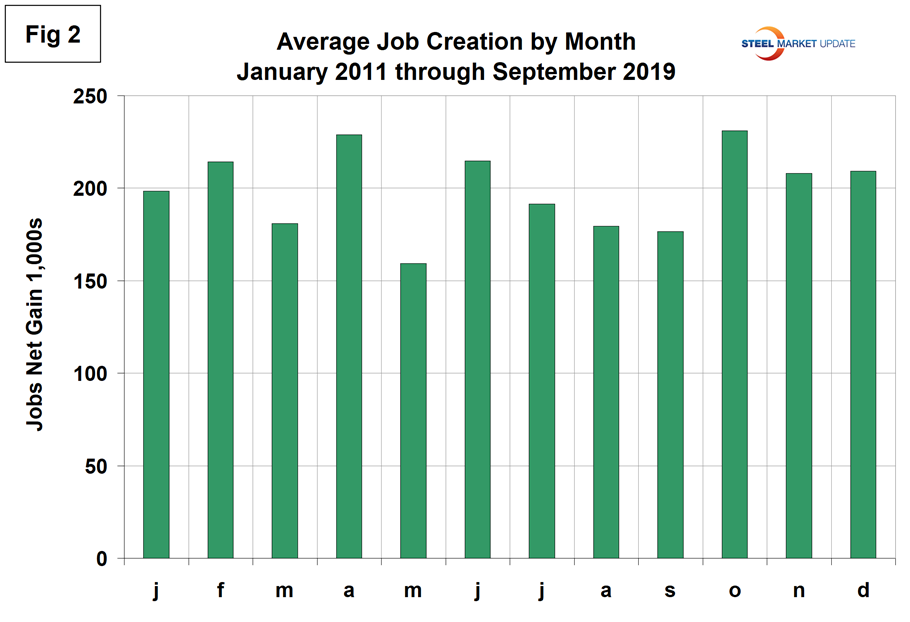
The employment data has been seasonally adjusted. We have developed Figure 2 to examine if any seasonality is left in the data after adjustment. In the nine years since and including 2011, the average month-on-month change from August to September has been negative 1.6 percent. This year the change was negative 19.0 percent, therefore worse than normal. We think it’s significant to look at the results this way because there is so much variability in the numbers that a long-term context is necessary and it doesn’t look as though the BLS’s seasonal adjustment is very effective.
In order to get another look at the degree of change, we have developed Figure 3. This shows the same total employment line as Figure 1, but includes the year-over-year growth on a percentage basis and shows more clearly the steady improvement that occurred during 2018 and the slowdown in 2019. The year-over-year growth of the total number employed has slowed from 1.9 percent in January 2019 to 1.4 percent in September. Considering the variability of the raw monthly data, we think the year-over-year view is the best way to evaluate what’s really going on.
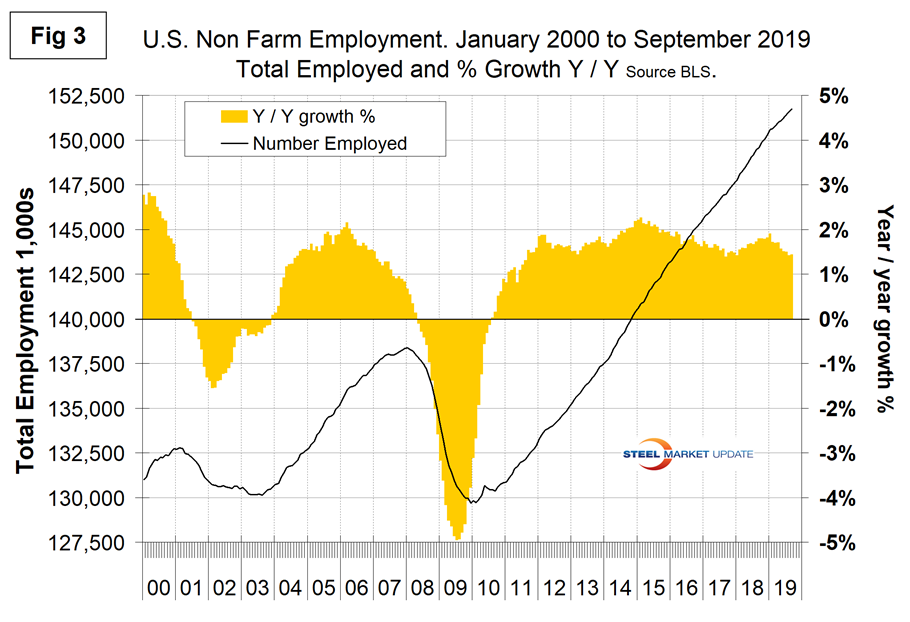
November 2018 was the first month ever for total nonfarm payrolls to exceed 150 million and in September 2019 was 151.722 million, which was 13.357 million more than the pre-recession high of January 2008.
According to the September BLS economic news release, average hourly earnings for all employees on private nonfarm payrolls, at $28.09, were little changed (-1 cent), after rising by 11 cents in August. Over the past 12 months, average hourly earnings have increased by 2.9 percent. In September, average hourly earnings of private-sector production and nonsupervisory employees rose by 4 cents to $23.65. The average workweek for all employees on private nonfarm payrolls was unchanged at 34.4 hours in September. In manufacturing, the average workweek and overtime remained at 40.5 hours and 3.2 hours, respectively. The average workweek of private-sector production and nonsupervisory employees held at 33.6 hours.
The official unemployment rate, U3, reported in the BLS Household survey (see explanation below) declined from 3.7 percent in June, July and August to 3.5 percent in September. U3 has ranged from 3.5 to 4.0 percent in each of the last 17 months. This is not a very representative number. The more comprehensive U6 unemployment rate at 6.9 percent was down from 8.1 percent in January (Figure 4). The difference between these two measures in September was 3.4 percent, which was the lowest since August 2001. U6 includes individuals working part time who desire full-time work and those who want to work but are so discouraged they have stopped looking.

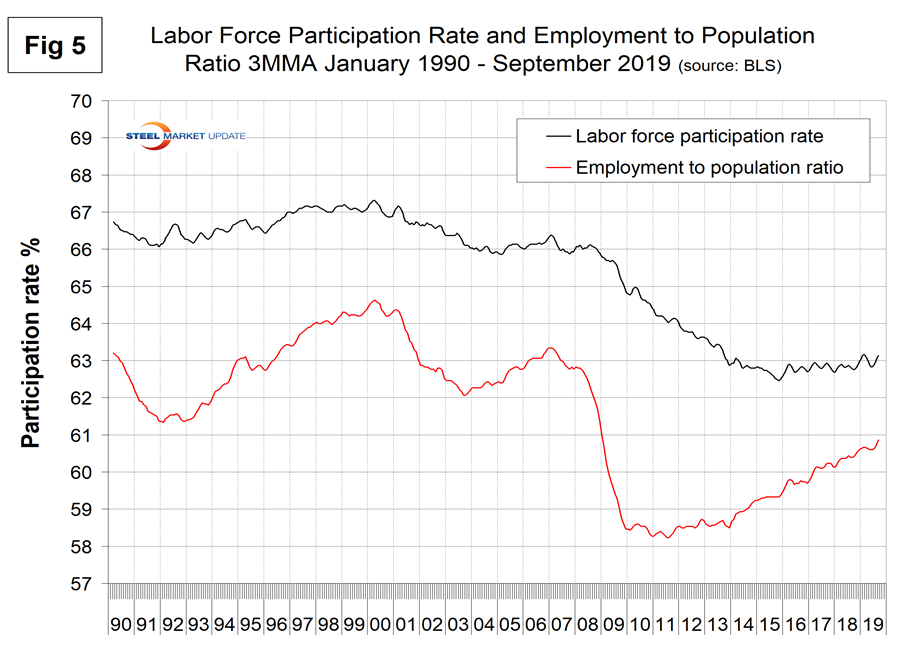
The labor force participation rate is calculated by dividing the number of people actively participating in the labor force by the total number of people eligible to participate. This measure was 63.2 percent in September and hasn’t changed much in three years. Another gauge is the number employed as a percentage of the population, which we think is more definitive. In September, the employment-to-population ratio was 61.0 percent, the highest since November 2008. Figure 5 shows both measures on one graph.
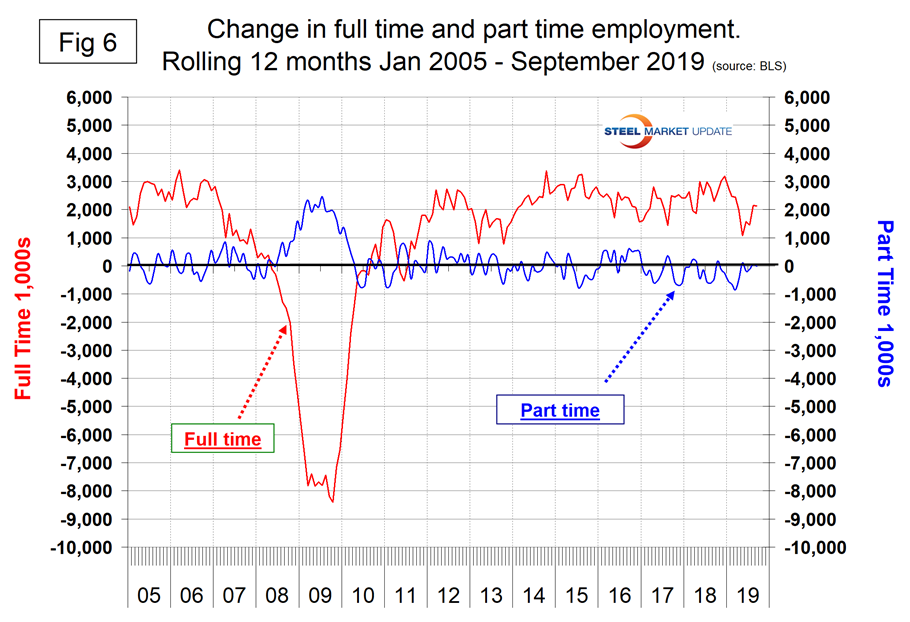
In the 45 months since and including January 2016, there has been an increase of 8,354,000 full-time and a decrease of 283,000 part-time jobs. Figure 6 shows the rolling 12-month change in both part-time and full-time employment. This data comes from the Household survey and part-time is defined as less than 35 hours per week. Because the full-time/part-time data comes from the Household survey and the headline job creation number comes from the Establishment survey, the two cannot be compared in any given month. To overcome the volatility in the part-time numbers, we look at a rolling 12 months for the full-time and part-time employment picture shown in Figure 6.
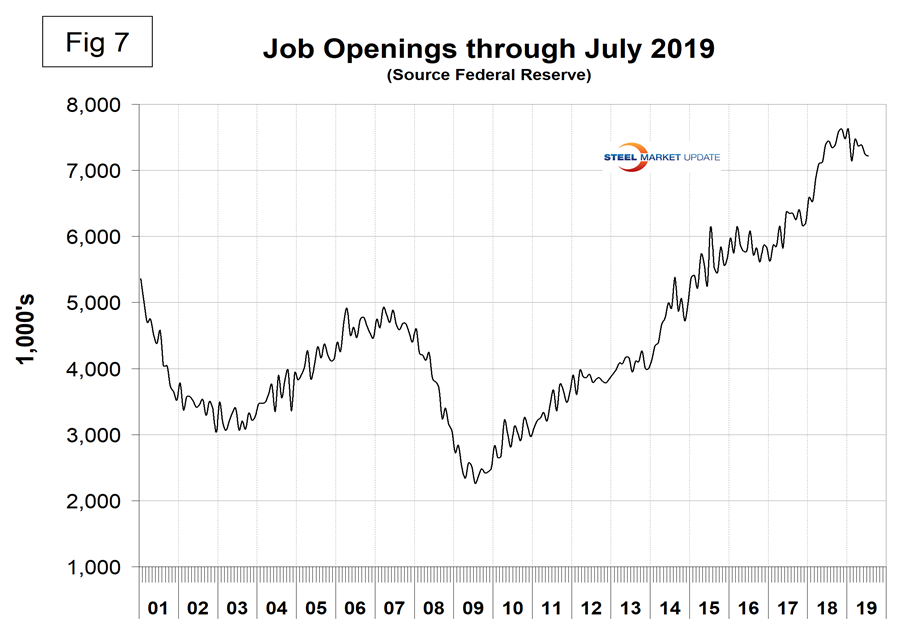
The job openings report known as JOLTS is reported on about the 10th of the month by the Federal Reserve and is over a month in arrears. In the September employment report, JOLTS data was reported for July. Figure 7 shows the history of unfilled jobs. In July, openings stood at 7,217,000, which was still historically very high. The all-time high was 7,626,000 in November 2018. There are now more job openings than there are people counted as unemployed.
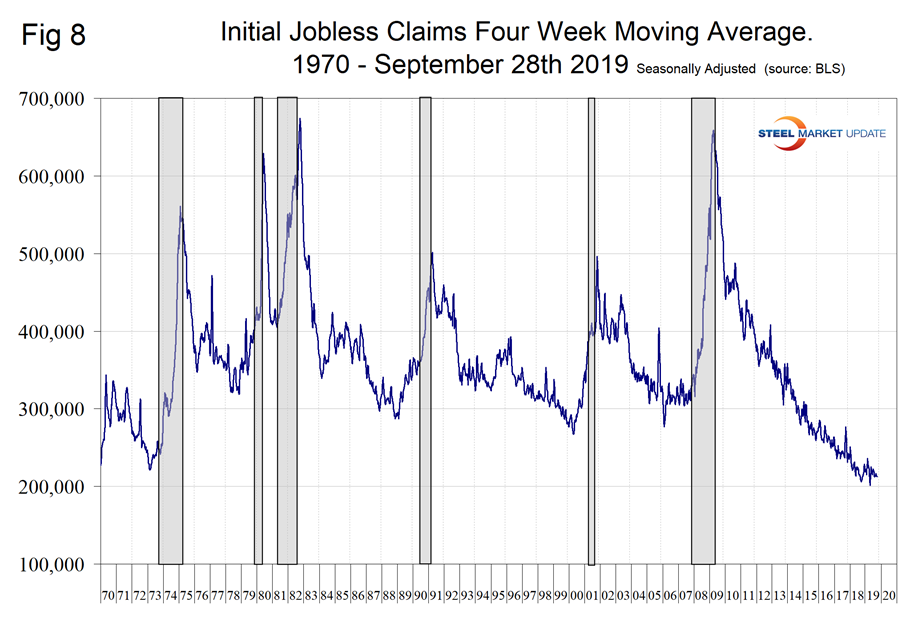
Initial claims for unemployment insurance, reported weekly by the Department of Labor, have been exceptionally low since 2014. The U.S. is enjoying the longest streak since 1973 of initial claims below 300,000 (Figure 8). This data stream is part of our recession outlook report and at present shows no sign of an imminent problem.
Challenger, Grey and Christmas produce a monthly report of job cuts in the U.S. Economy.com reported: “Job cuts fell to 41,557 in September, down 22% from the previous month. This also marks a 25% drop from a year earlier. Retail, industrial goods and automotive ranked highest in job cuts by industry. Collectively, the three industries accounted for 44% of announced layoffs. Firms reported branch closings and bankruptcies as the most common reasons for layoffs in September. Companies listed more than 2,500 job cuts related to labor disputes, reflecting the effects of the General Motors strike on auto parts suppliers and other downstream industries.”
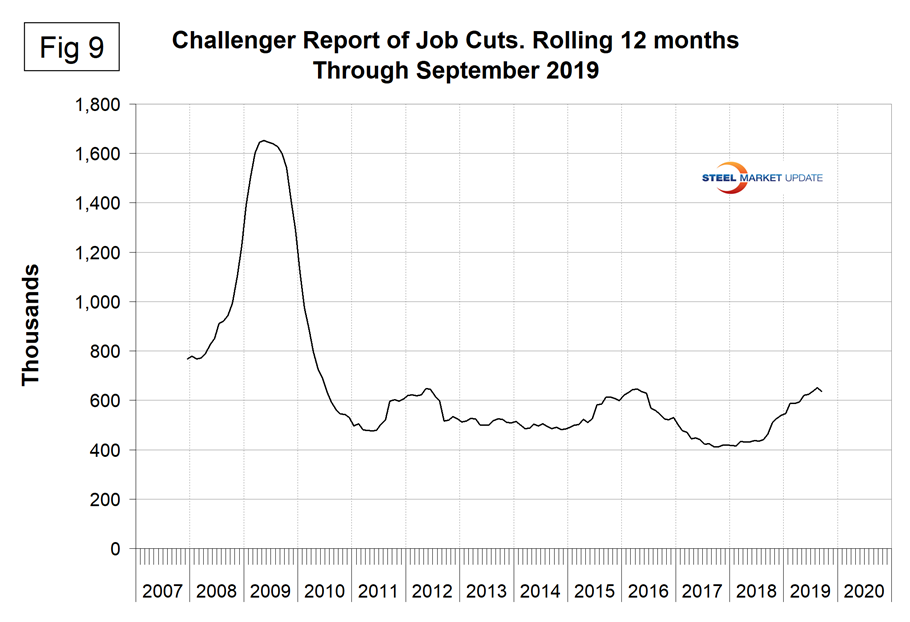
SMU Comment: In assessing the state of the labor market, it is necessary to look at longer time frames than one month because of the extreme volatility of the data. Job openings are very high and new unemployment claims are very low. This was not a bad report, but it is clear that the rate of job creation has slowed continuously in 2019.
Explanation: On the first Friday of each month, the Bureau of Labor Statistics releases the employment data for the previous month. Data is available at www.bls.gov. The BLS reports on the results of two surveys. The Establishment survey reports the actual number employed by industry. The Household survey reports on the unemployment rate, participation rate, earnings, average workweek, the breakout into full-time and part-time workers and lots more details describing the age breakdown of the unemployed, reasons for and duration of unemployment. At Steel Market Update, we track the job creation numbers by many different categories. The BLS database is a reality check for other economic data streams such as manufacturing and construction. We include the net job creation figures for those two sectors in our “Key Indicators” report. It is easy to drill down into the BLS database to obtain employment data for many subsectors of the economy. For example, among hundreds of sub-indexes are truck transportation, auto production and primary metals production. The important point about all these data streams is the direction in which they are headed. Whenever possible, we try to track three separate data sources for a given steel-related sector of the economy. We believe this gives a reasonable picture of market direction. The BLS data is one of the most important sources of fine-grained economic data that we use in our analyses. The states also collect their own employment numbers independently of the BLS. The compiled state data compares well with the federal data. Every three months, SMU examines the state data and provides a regional report, which indicates strength or weakness on a geographic basis. Reports by individual state can be produced on request.







