Market Data

June 2, 2019
Active Gas & Oil Rig Counts
Written by Brett Linton
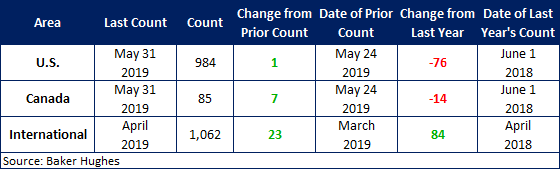
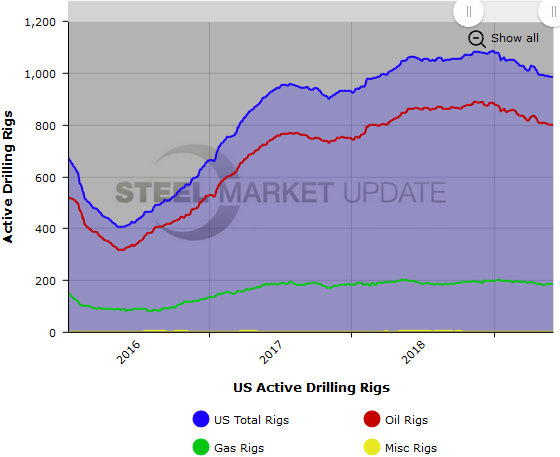
The U.S. active rotary rig count, an indicator of oil country tubular goods demand, increased this week, according to oilfield services company Baker Hughes. The number of active U.S. rigs rose by 1 to 984, with oil rigs up 3 and gas rigs down 2. Compared to this time last year, the 984 count is down 76 rigs, with oil rigs down 61, gas rigs down 13, and miscellaneous rigs down 2. See the first graph below for a history of active U.S. rig counts.
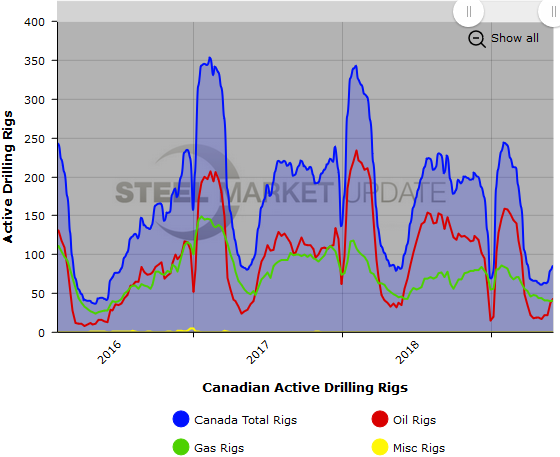
The Canadian rig count rose by 7 to 85 rigs, with oil rigs up 6 and gas rigs up 1. Compared to last year, the 85 count is down 14 rigs, with oil rigs down 12 and gas rigs down 2. See the second graph below for a history of active Canadian rig counts.
International rigs increased by 23 to 1,062 rigs for the month of April, an increase of 84 rigs from the same month one year ago. For a history of both the U.S. and Canadian rig count, visit the Rig Count page on the Steel Market Update website here.
About the Rotary Rig Count
A rotary rig is one that rotates the drill pipe from the surface to either drill a new well or sidetrack an existing one. They are drilled to explore for, develop and produce oil or natural gas. The Baker Hughes Rotary Rig count includes only those rigs that are significant consumers of oilfield services and supplies.
The Baker Hughes North American Rotary Rig Count is a weekly census of the number of drilling rigs actively exploring for or developing oil or natural gas in the United States and Canada. Rigs considered active must be on location and drilling. They are considered active from the time they break ground until the time they reach their target depth.
The Baker Hughes International Rotary Rig Count is a monthly census of active drilling rigs exploring for or developing oil or natural gas outside of the United States and Canada. International rigs considered active must be drilling at least 15 days during the month. The Baker Hughes International Rotary Rig Count does not include rigs drilling in Russia or onshore China.