Sheet
December 11, 2024
US HR tags slip, premium over landed imports narrows
Written by David Schollaert
Hot-rolled (HR) coil prices ticked back down in the US this week, while tags in offshore markets were mostly up. Thus, the price premium between stateside hot band and imports on a landed basis contracted slightly.
This week, variations across domestic and overseas markets cut the US price premium a bit.
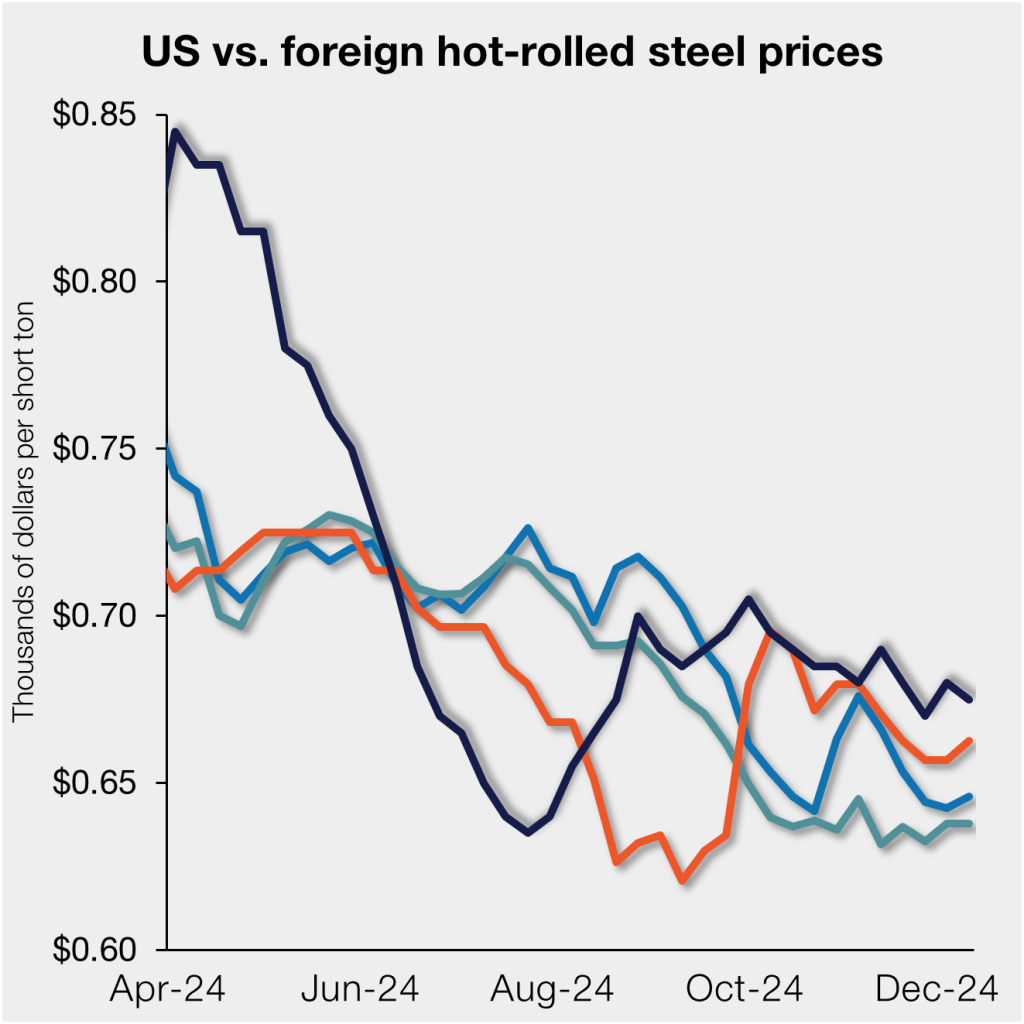
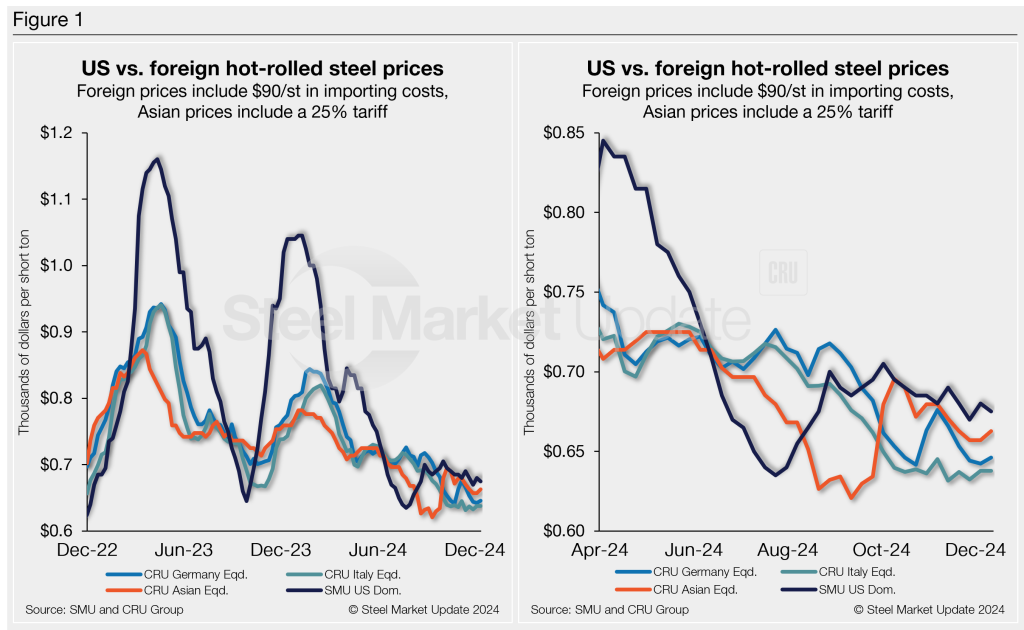
SMU’s check of the market on Tuesday, Dec. 10, put average domestic HR tags at $675 per short ton (st), down $5/st from the week before. US hot band did rebound from a 20-month low of $635/st in late July, but prices have not shifted much, averaging $682/st since.
Domestic HR is now theoretically 3.9% more expensive than imported material, down from last week’s reading of 5%. While increases in the premium have been insignificant at times, and US prices are still marginally higher, and ahead of late July when stateside products were ~12% cheaper than imports.
In dollar-per-ton terms, US HR is now, on average, $26/st more expensive than offshore product (see Figure 1). That’s up down $8/st from last week and about $98/st from late July when US tags were ~$72/st cheaper than offshore material.
The charts below compare HR prices in the US, Germany, Italy, and Asia. The left-hand side highlights prices over the last two years. The right-hand side zooms in to show more recent trends.
Methodology
This is how SMU calculates the theoretical spread between domestic HR coil prices (FOB domestic mills) and foreign HR coil prices (delivered to US ports): We compare SMU’s weekly US HR assessment to the CRU HR weekly indices for Germany, Italy, and East and Southeast Asian ports. This is only a theoretical calculation. Import costs can vary greatly, and that can influence the true market spread.
We add $90/st to all foreign prices as a rough means of accounting for freight costs, handling, and trader margin. This gives us an approximate CIF US ports price to compare to the SMU domestic HR coil price. Buyers should use our $90/st figure as a benchmark and adjust up or down based on their own shipping and handling costs. If you import steel and want to share your thoughts on these costs, please get in touch with the author at david@steelmarketupdate.com.
Asian HRC (East and Southeast Asian ports)
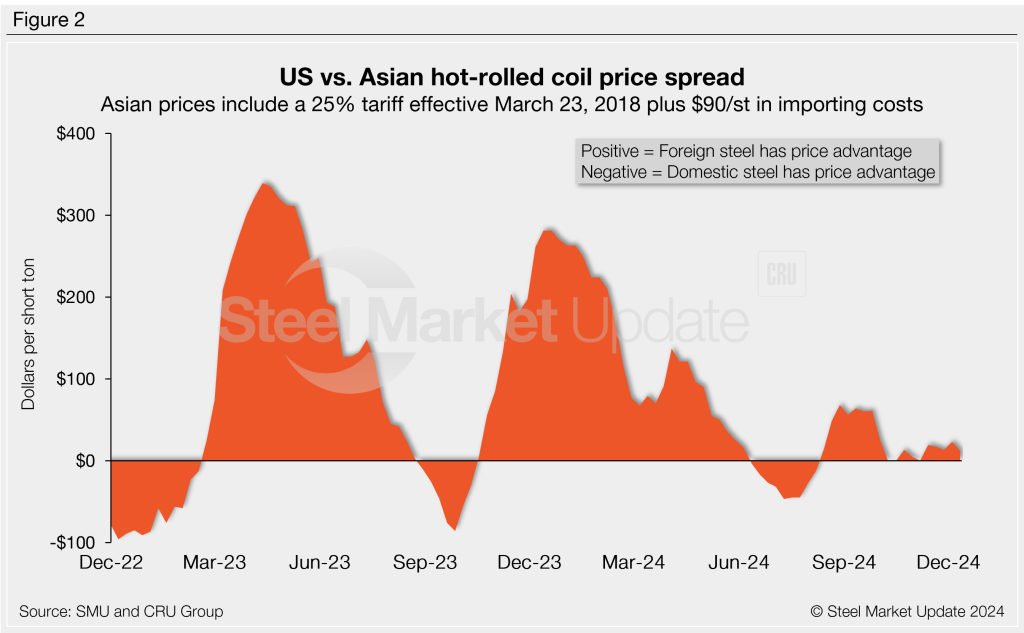
As of Wednesday, Dec. 11, the CRU Asian HRC price was $458/st, up $4/st vs. the week prior. Adding a 25% tariff and $90/st in estimated import costs, the delivered price of Asian HRC to the US is approximately $663/st. As noted above, the latest SMU US HR price is $675/st on average.
The result: Prices for US-produced HR are theoretically $12/st higher than steel imported from Asia. Despite the week-over-week (w/w) decrease in the premium, it is still significantly lower than last December when US HR was $281/st more expensive than Asian products.
Italian HRC
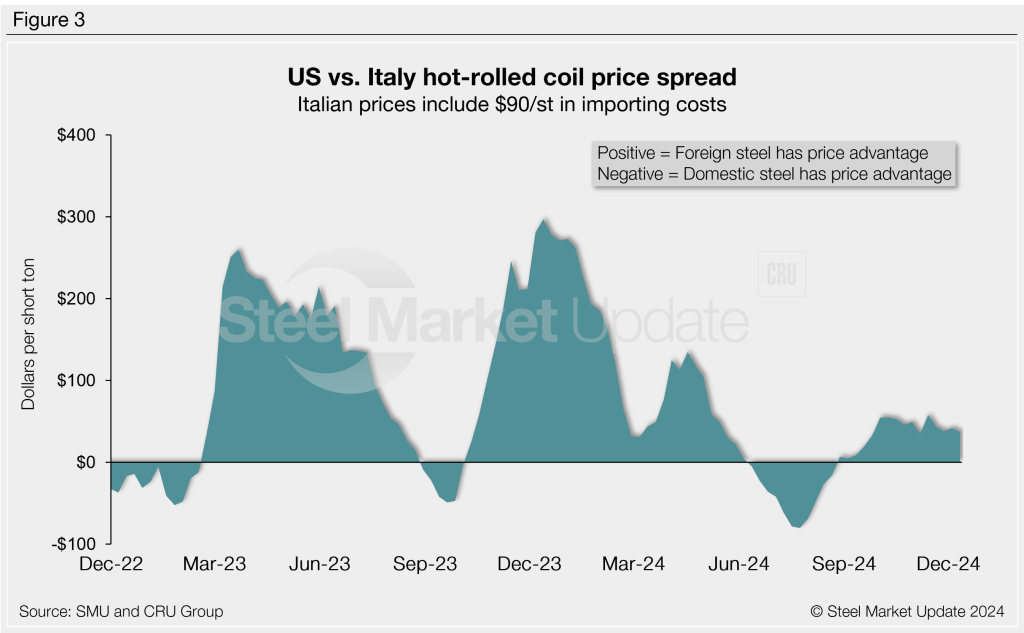
Italian HR prices were flat this week at $548/st, according to CRU. After adding import costs, the delivered price of Italian HR is, in theory, $638/st.
That means domestic HR coil is theoretically $37/st more expensive than imports from Italy. The spread is down $5/st w/w as US tags slipped vs. Italian prices. Recall that US HR was $297/st more costly than Italian hot band about six months ago.
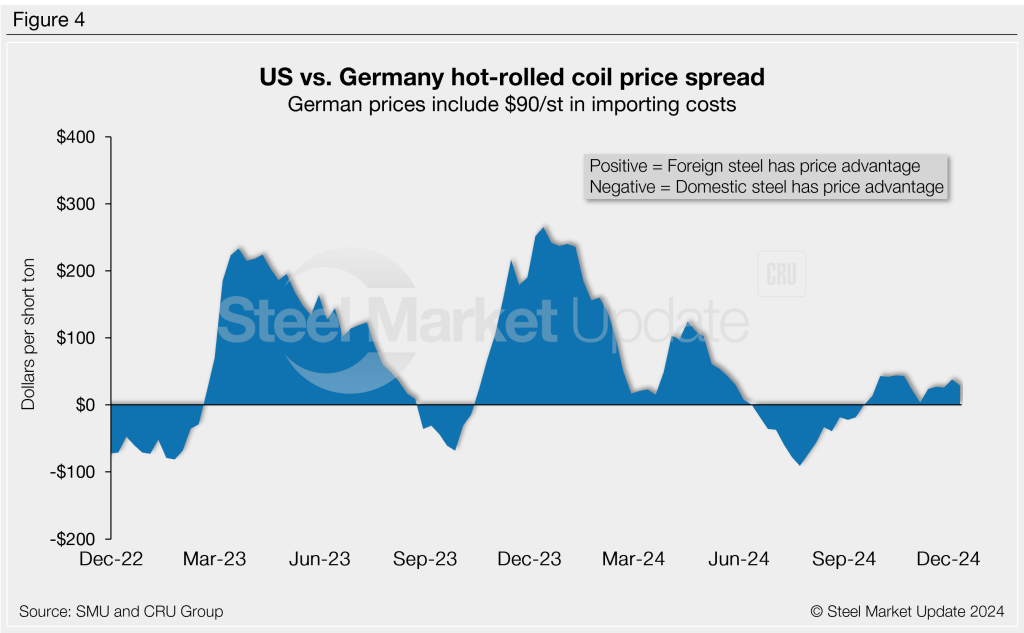
German HRC
CRU’s German HR price moved up $4/st to $556/st this week. After adding import costs, the delivered price of German HR coil is, in theory, $646/st.
The result: Domestic HR is theoretically $29/st more expensive than HR imported from Germany, down $9/st from last week. Stateside hot band was at an $18/st discount about three months ago. At points in 2023, in contrast, US HR was as much as $265/st more expensive than imported German hot band.
Notes: Freight is important when deciding whether to import foreign steel or buy from a domestic mill. Domestic prices are referenced as FOB the producing mill. Foreign prices are CIF, the port (Houston, NOLA, Savannah, Los Angeles, Camden, etc.). Inland freight, from either a domestic mill or from the port, can dramatically impact the competitiveness of both domestic and foreign steel. It’s also important to factor in lead times. In most markets, domestic steel will deliver more quickly than foreign steel. Effective Jan. 1, 2022, Section 232 tariffs no longer apply to most imports from the European Union. It has been replaced by a tariff rate quota (TRQ). Therefore, the German and Italian price comparisons in this analysis no longer include a 25% tariff. SMU still includes the 25% Section 232 tariff on prices from other countries. We do not include any antidumping (AD) or countervailing duties (CVD) in this analysis.







