Government/Policy

March 15, 2018
Mitigating Costs and Risks of Section 232 Tariffs
Written by Sandy Williams
Much has been made of the damage the Section 232 actions may have on the economy and individual firms, but little has been said about how to mitigate costs and manage risks from the tariffs. Donald Bly, Associate Partner at Applied Value, LLC, a New York management consulting and investment group, offers some strategies on how to address President Trump’s recent tariff announcement.
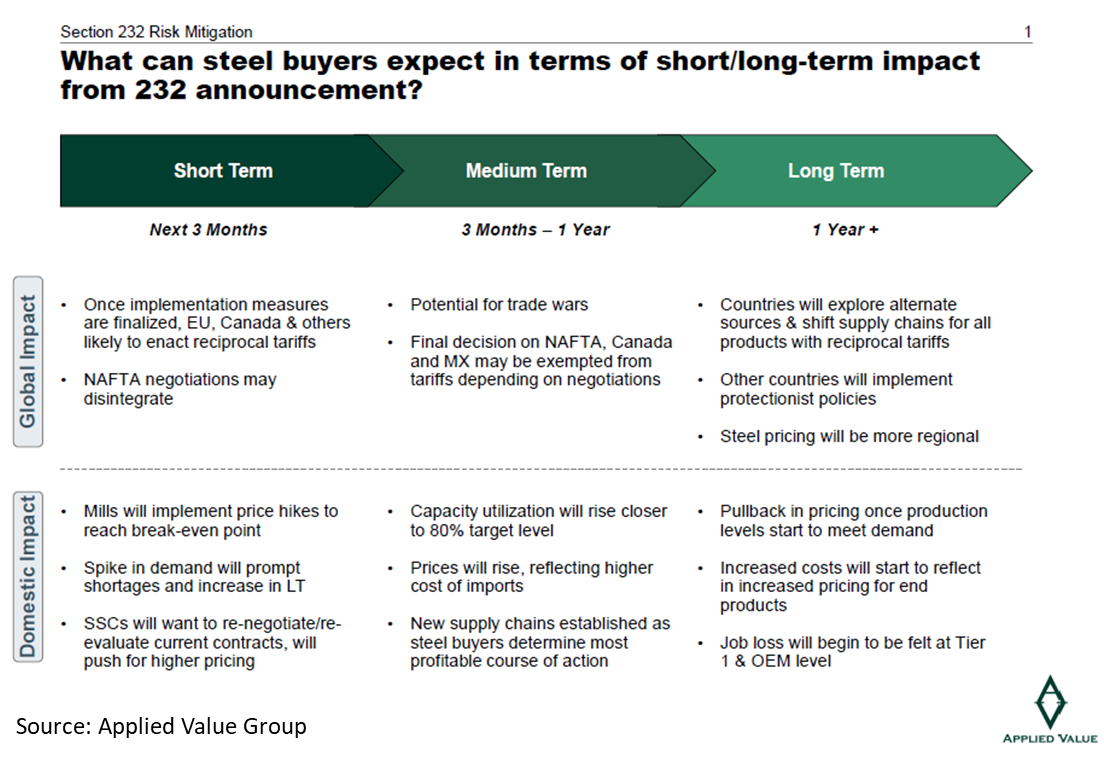
The exemption of Canada and Mexico from the tariffs will help “release some of the supply and demand pressure that the tariffs will generate in the U.S. domestic market and lead to slightly less drastic lead time elongation and price increases,“ Bly said. The exemptions also will give firms the opportunity to continue trade within the North American value chain.
Steel futures prices for April declined slightly because of the exemptions, but spot pricing continues to rise. Buyers can expect significantly higher steel prices in 2018 than 2017, Bly said.
In the short term, Canadian and Mexican steel prices will rise, but not as much as U.S. prices. Prices in Europe are expected to increase as mills “attempt to capitalize on U.S. increases to buoy their own price hikes.”
“Steel pricing dynamics are regional, but heavily influenced by global markets, and EU mills will use this to their advantage—although further protectionism will reduce the global influence,” said Bly.
U.S. manufacturers and buyers will need to implement mitigation strategies against cost inflation and a “dramatic impact” to gross margins. As a result, less investment by OEMS and fabricators will occur due to higher costs of production, and more firms will potentially move production overseas, Bly said. One example is Electrolux, which delayed a $250 million investment in the U.S.
Downstream job losses will increase significantly compared to the growth of U.S. steel mill jobs, Bly said. For each job lost at an OEM producer, there will be from one to 25 additional jobs lost upstream at Tier 1 companies and their service providers, he estimates.
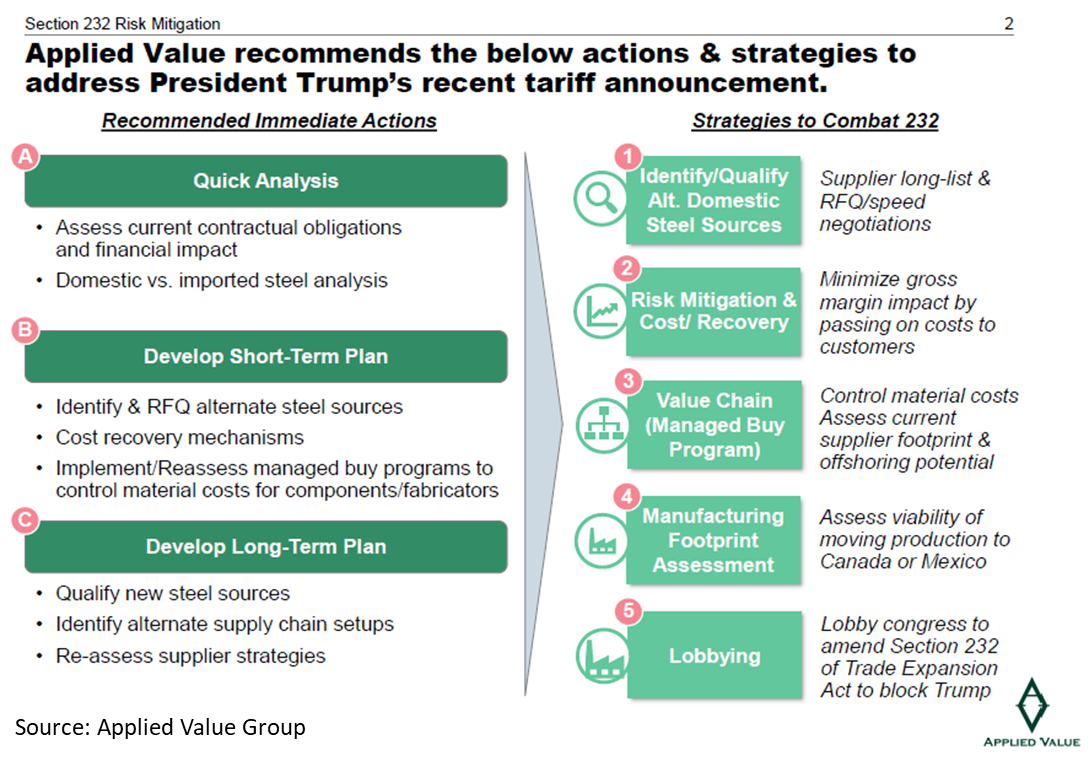
Bly suggests companies take three immediate actions to address Section 232 concerns: Do a quick analysis of contractual obligations and financial impact, as well as domestic versus imported steel use. Develop a short-term plan that includes obtaining quotes from alternate steel sources, identifying cost recovery mechanisms and implementing managed buy programs to control material costs. Then, develop a long-term plan that includes qualifying new steel sources, identifying alternate supply chains and reassessing supplier stategies.